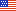
Components of State Anti-Bullying Laws and Regulations
| Component | Included |
|---|---|
| Prohibiting statement | Yes |
| Definition | Yes |
| Scope | Yes |
| Protected groups | No |
| District policy requirement | Yes |
| Reporting and investigations | Yes |
| Consequences | Yes |
| Communication of policy | Yes |
| Safeguards and supports | Yes |
| Review and update of local policies | Yes |
| Prevention education | Yes |
| Staff training | Yes |
| Parent engagement | Yes |
Which Ohio laws and regulations cover bullying?
- Ohio Revised Code Annotated §5.2296. School Bullying Prevention and Awareness Act
- Ohio Revised Code Annotated §117.53. Audit statement regarding adoption of anti-harassment policy
- Ohio Revised Code Annotated §2307.44. Hazing civil liability
- Ohio Revised Code Annotated §2903.31. Hazing
- Ohio Revised Code Annotated §3301.22. Model harassment prevention policy
- Ohio Revised Code Annotated §3313.6024. Reporting on prevention-focused programs
- Ohio Revised Code Annotated §3313.666. District policy prohibiting harassment, intimidation, or bullying required
- Ohio Revised Code Annotated §3313.667. District bullying prevention initiatives
- Ohio Revised Code Annotated §3319.073. In-service training in child abuse prevention programs, school safety and violence prevention, and training on the board's harassment, intimidation, or bullying policy
- Ohio Revised Code Annotated §4503.723. “Stop Bullying” license plates
How are bullying and cyberbullying defined in Ohio anti-bullying laws and regulations?
Ohio anti-bullying laws include the following definitions of harassment, intimidation, and bullying:
“Harassment, intimidation, or bullying” means either of the following:
(a) Any intentional written, verbal, electronic, or physical act that a student has exhibited toward another particular student more than once and the behavior both:
(i) Causes mental or physical harm to the other student;
(ii) Is sufficiently severe, persistent, or pervasive that it creates an intimidating, threatening, or abusive educational environment for the other student.
(b) Violence within a dating relationship.
Ohio Rev. Code Ann. § 3313.666 (2012)
Do Ohio anti-bullying laws and regulations cover cyberbullying that occurs off-campus?
No. Ohio anti-bullying laws do not cover off-campus conduct.
What are the policy requirements for schools to prevent and respond to bullying behavior?
Ohio school districts must establish a policy prohibiting harassment, intimidation, or bullying. School district policies must contain key policy and procedural elements, including, but not limited to:
- Statements prohibiting harassment, intimidation, or bullying and statements of scope indicating where and when the policy applies;
- Definitions of prohibited behavior that are inclusive of definitions in state law;
- Procedures for reporting, investigations, and documentation;
- Strategies for protecting a victim or other person from harassment, intimidation, or bullying or from retaliation following a report;
- Disciplinary consequences for violation of the policy;
- Statements prohibiting students from making false reports;
- Statements of how the policy will be publicized within the district; and
- Requirements that districts provide a written summary of all report incidents and post the summary on the district website.
Ohio state school district audits include a review of whether a school district has adopted a policy prohibiting harassment, intimidation, or bullying.
Do Ohio anti-bullying laws and regulations include protections for specific groups?
No. There are no specific groups listed under Ohio anti-bullying laws or regulations.
Schools that receive federal funding are required by federal law to address discrimination based on certain personal characteristics. Find out when bullying may be a civil rights violation.
Do Ohio anti-bullying laws and regulations encourage or require districts to implement bullying prevention programs or strategies?
Yes. Ohio anti-bullying laws encourage districts to form bullying prevention task forces, programs, and other initiatives involving volunteers, parents, law enforcement, and community members. Ohio school districts must also report to the state Department of Education the types of prevention-focused programs, services, and supports used to assist students in developing the knowledge and skills to engage in healthy behaviors and decision-making and to increase their awareness of risky behaviors, including substance abuse, suicide, bullying, and other harmful behaviors.
Do Ohio anti-bullying laws and regulations encourage or require districts to train teachers and other school staff on how to respond to bullying incidents?
Yes. Ohio anti-bullying laws require each board of education to incorporate training on the board’s harassment, intimidation, or bullying policy into in-service training programs. Ohio anti-bullying laws also require districts to provide training, workshops, or courses on the district’s harassment, intimidation, or bullying policy to school employees and volunteers who have direct contact with students and who are not subject to other in-service training requirements, to the extent that state or federal funds are appropriated for these purposes.
Do Ohio anti-bullying laws and regulations encourage or require districts to provide safeguards or mental health supports for students involved with bullying?
Yes. Ohio anti-bullying laws require districts to develop policies that include strategies for protecting a victim or other person from new or additional harassment, intimidation, or bullying and from retaliation following a report.
Do Ohio anti-bullying laws and regulations involve parents in efforts to address bullying behavior?
Yes. Ohio anti-bullying laws require districts to develop policies in consultation with parents, school employees, school volunteers, students, and community members. Ohio school district policies must include a requirement that the custodial parent or guardian of any student involved in a prohibited incident be notified and be given access to any written reports pertaining to the prohibited incident to the extent permitted by state and federal law.
For More Information
Visit the Ohio Department of Education’s “Anti-Harassment, Intimidation and Bullying Resources” webpage and/or view the Ohio state model policy on bullying and harassment.
The key component framework used in the analysis of state laws is based on the review of legislation presented in the “Analysis of State Bullying Laws and Policies – December 2011” (U.S. Department of Education).